Video Editing Terms & Concepts Explained (Full 2026 Glossary)
A complete glossary of video editing terms for creators. Understand timelines, rough cuts, assembly edits, post-production workflows, and modern AI video editing.

Video editing can feel like a different language. Between stringouts, assembly cuts, timelines, and non-destructive editing, the terminology stacks up fast, especially now that AI workflows are changing how video production and post production actually happen day-to-day.
But what is video editing really? This glossary explains the essential editing terms every creator should know, whether you’re learning what video editing really is at its core or leveling up your storytelling with modern tools. From the first rough cut to final delivery, here’s your complete guide to how editors think, work, and bring a project to life.
Why This Glossary Matters for Video Editors & Creators
Editing jargon can feel gatekeep-y. But once you understand the fundamentals and video editing basics such as timeline structure, how cuts evolve, and what editors actually do, your creative decisions get faster and more intentional.
This page breaks down the terms editors use daily, with real examples from YouTube, podcasts, and AI-enabled workflows.
Video Editing Glossary: Core Video/Film Editing Terms Every Creator Should Know
Timeline

The timeline is where video editing actually happens. It’s the layered workspace inside NLEs like Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro. Video editing software like Selects might boast unconventional timelines, too.
How to read a timeline:
Top tracks = video (main camera, B-roll, graphics)
Bottom tracks = audio (dialogue, music, sound effects)
Time flows left → right
Editors spend almost their entire workflow shaping:
pacing for impactful storytelling
shot selection to ensure the best visuals, timing, and flow
managing sound quality
imagining the viewer experience
The timeline is the heart of video editing, where raw footage becomes a watchable story.
Stringout

What is a stringout? A stringout is a long timeline where you keep every usable clip in sequence, no heavy editing yet.
The purpose of a stringout:
Review all material in context
Understand the story flow from start to finish
Prevent missing hidden gems or great reactions
Commonly used to edit:
Interviews
Documentaries
Podcast episodes
A stringout is not polished, but it gives you a crucial first look at the full story before making creative decisions.
A stringout reveals the entire narrative structure before the rough cut begins.
Selects

Selects are the best-performing clips pulled from the stringout into a cleaner timeline. They remove noise and keep only the moments worth refining.
What goes into selects:
Clear answers
Laughs or reactions
Emotional peaks
Visual interest
Key teaching moments
They make the editing process faster and smarter, especially for long-form shoots.
Selects help editors avoid digging through hours of footage again; only the highlights move forward.
Make sure to check out this comparison of the difference between selects and a stringout.
Sequence
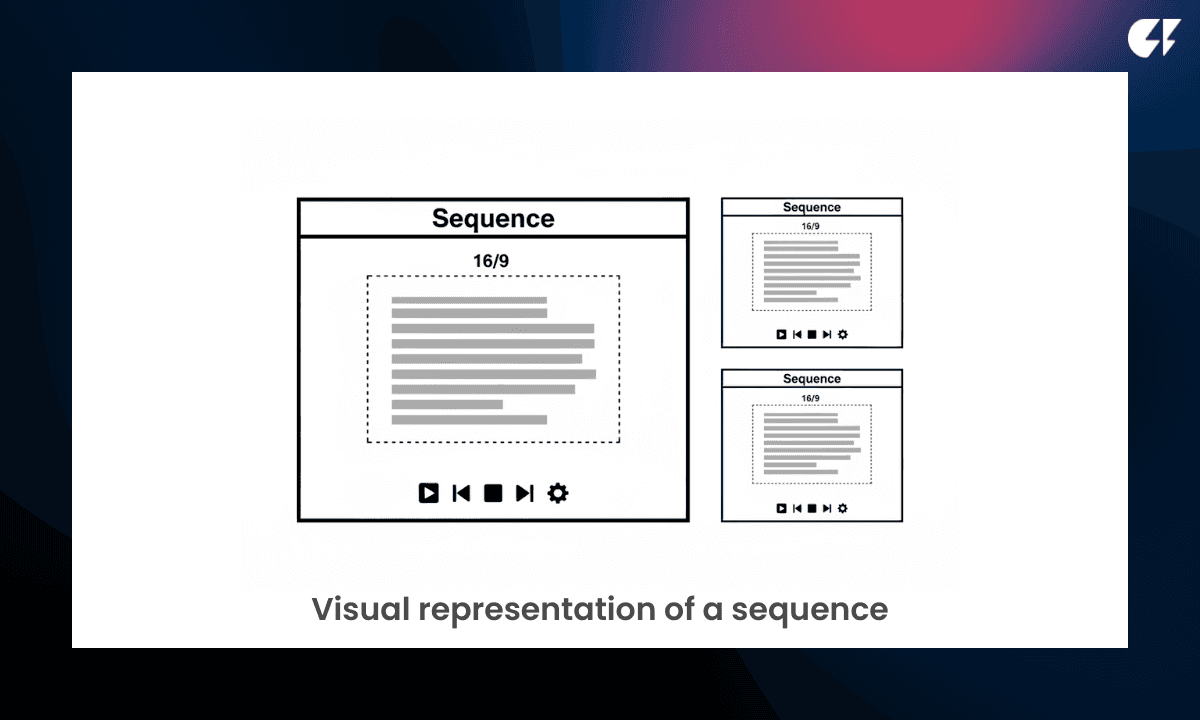
A sequence is a project container inside your NLE where your timeline lives.
Video editing technicalities defined in the sequence:
Resolution (1080p, 4K, etc.)
Frame rate (24/30/60 fps)
Aspect ratio (16:9, 9:16, 1:1)
You might create multiple sequences for:
Different versions of the same video
Short-form vs. long-form outputs
Revisions for clients
Every major storytelling decision exists inside a sequence.
A sequence is your canvas for editing, a flexible space for different versions and deliverables.
Editing Workflow Terms
Assembly Cut (or Assembly Edit)
The assembly cut is the first fully watchable version of a video. All usable clips are placed in timeline order based on the script or interview flow, but nothing is polished yet.
What to expect:
Loose pacing
Repeated lines or unfinished thoughts
Minimal trimming
No music, graphics, or proper audio mix yet
This is the stage where you verify the story exists. Editors and producers watch it to ensure the structure makes sense before refining anything.
The assembly cut gives you your first look at what the final video could be, without wasting time polishing pieces that might still get cut. Done mostly manually before, AI assembly cut video editors are now automating this process.
Rough Cut
The rough cut is where the story gets locked. Major trims happen here: awkward pauses, off-topic tangents, and distracting shots are removed.
These are the aspects that are improved in a rough cut:
Pacing and flow
Emotional beats (timely reactions, punchlines, key insights)
Music temped in for tone
Early version of cutaways/B-roll
But still no final audio mix, color grade, or animated graphics.
The rough cut is where the video finally feels like a real edit, even though technical finishing hasn’t started yet.
Final Cut
Nearly finished. This is when you would use more advanced editing skills instead of just cutting.
The final video cut is where you would:
Color grade - Enhance the look of your video by adjusting contrast, colors, and lighting so the final product feels cinematic and consistent across all shots.
Audio mix - Balance dialogue, music, and sound effects to ensure clear voices, clean transitions, and a polished listening experience on every platform.
Lock in graphics - Add and finalize titles, captions, lower thirds, and visual overlays that communicate key information and keep the viewer engaged.
At this stage, changes are expensive and annoying for your editor.
Paper Cut
If you’ve ever wondered about the meaning of a paper cut in film…. It’s a script-based plan of what the edit will be, before touching footage (or sometimes after the first rough cut to give feedback on changes). It often contains notes from the director, producer, or editor of editing changes to make or pay attention to based on observations from filming.
Traditionally done in Google Docs / Notion.
Modern version: AI-driven organization tools like Selects can automate the paper cut by tagging topics and choosing relevant clips.
Creative Concepts In Video Editing Terminology
Vibe Editing
If you have ever wondered, “What is vibe editing?” you’ve come to the right place. It’s cutting based on emotion and viewer engagement instead of a strict script, usually done with the assistance of AI to supplement editing knowledge or bandwidth. Vibe editing takes on new ways of editing, to lessen the learning curve, such as using chat-based video editing through chat UIs (known as ChatGPT video editing app styles) and interfaces.
Popularly used for editing the following types of content:
Solo content creator videos (long-form YouTube videos, Instagram Reels, TikToks, etc.)
Raw-footage heavy content styles like podcasts, documentaries, and interviews
Event videos with dialogue-heavy moments (weddings, conferences, etc.)
Non-Destructive Editing
Your original footage is never overwritten.
Everything lives as options rather than permanent changes.
Hitting the undo button is always possible.
This is essential for:
• Collaboration (with other video editors, or co-editing video agents)
• Version control (have access to previous versions of your video edit)
• Multicam workflows (especially for multi-camera switching)
Industry Editing Roles & Responsibilities
Understanding how post-production teams divide work helps creators collaborate better or structure their own workflow if they’re solo.
Editors are the creative owners of the story. They shape pacing, emotion, clarity, and entertainment value, not just trimming clips. They decide what stays, what goes, and why. In film and TV, they work closely with directors. In YouTube and brand content, they collaborate directly with creators.
Entry-Level Roles
Assistant Editor (AE)
Technical and workflow foundation
• Audio sync + multicam prep
• Building stringouts and selects
• File organization + media management
• Fixing timeline issues
• Exporting and deliverables
AI tools like Selects are automating the AE workflow, letting more creators skip this step.
Junior Editor
Developing creative judgement under guidance
• Takes over first passes on simpler content
• Works from a rough cut handed down by a senior/editor
• Learns pacing, comedic timing, narrative flow
• Receives lots of review cycles
Success metric: Learn speed → then learn taste
Experienced Roles
Senior Editor
Creative leadership + mentorship
• Sets editing style and story philosophy
• Oversees multiple editors on a series or brand
• Approves picture lock
• Can “fix” any struggling edit
• Trusted with highest-impact projects
At this stage, taste is the job.
How These Terms Fit Together in a Real Workflow Using Editing Techniques
A typical video goes through these stages:
Scripts & storyboards → plan the story and the visuals
Paper cut → text-based outline of what will stay, go, or move before touching the timeline
Stringout → everything in order
Selects → only the usable moments
Assembly Cut → usable moments put together in a first cut
Rough Cut → involves more video editing technique and pacing fixes
Final Cut → polished and approved
Delivery → exports for YouTube, Shorts, etc.
This creates a shared language so editors and creators can collaborate without confusion.
Keep Learning with Modern Editing Workflows
If you're leveling up as a creator, editing jargon should never slow you down.
Explore these next:
• AI Editing Workflows for Content Creators
• AI Video Editing: Complete Guide
• AI Podcast Video Editing Guide
For more in-depth knowledge about the ins and outs of video editing, check out our latest posts on the Cutback blog or our YouTube channel.

Kay Sesoko
Marketer
Share post